Smart Factories in Plastics Processing

Smart factories use data analytics, automation, and modular design to enhance efficiency, adaptability, and sustainability in plastics manufacturing.
The term “smart factory” refers to the modernization and improvement of manufacturing processes through the use of innovative technologies. Data analytics, automation, and modular structures are three key objectives of the smart factory concept. Within the plastics industry, automation is of particular interest to manufacturers. Injection molding, for example, offers high potential for automation. The smart factory concept can provide manufacturers with a framework for implementing technological goals to enhance both output and sustainability.
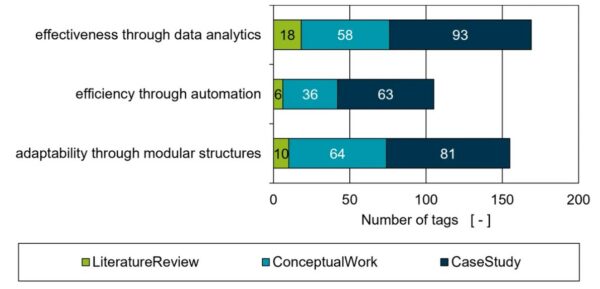
Through a literature review, researchers found that data analytics, automation, and modular structures were three vital pillars of “smart factories.” Figure courtesy of Smart factory concepts and their fitness to the plastics processing industry: a critical review.
Data Analytics: Enabling Communication
By collecting, processing, and analyzing data, manufacturers can create communication pathways between processes and optimize workflows. Various technologies can provide data acquisition and communication solutions tailored to the needs of the manufacturing environment. Then, advanced models, such as those using generative artificial intelligence (AI), can process these data to provide key insights. Such insights could include preventative maintenance information, optimized injection molding parameters, or energy consumption visualizations.
Automation: Increasing Efficiency
A smart factory should leverage automation to increase process efficiency and product quality. For example, manufacturers can use order processing systems to limit human error when scheduling, executing, and monitoring manufacturing processes. Additionally, edge devices can process sensor signals to interpret data in real-time, allowing for immediate action.
You can also read: Industrial Automation: Cloud Asset Integration for Smart Manufacturing
Modular Structures: Ensuring Adaptability
Through modular, reconfigurable software structures, manufacturers can more readily adapt to changes in customer and market demands. Web services and cloud applications can enable manufacturers to achieve a modular business software environment. This allows manufacturers to maintain organizational agility in a changing market.
Smart Factories in the Plastics Industry
Process digitization is key in establishing a smart factory. Already, many plastic processing machines and peripherals use Open Platform Communication Unified Architecture (OPC UA) cross-industry machine communication. Additional technologies can enhance already existing machinery communication features.
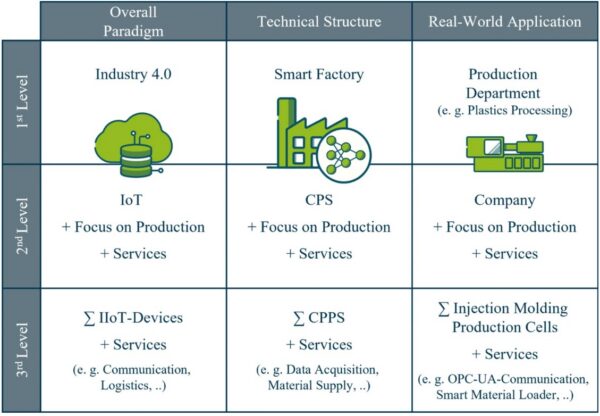
Through the implementation of new technologies, manufacturers actualize the smart factory concept. Figure courtesy of Smart factory concepts and their fitness to the plastics processing industry: a critical review.
Automation of order processing and quality control systems can benefit manufacturers, also supporting smart factory initiatives. Interfacing with software such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems can bolster capabilities of Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES). There are many technological solutions available on the market for plastics processors interested in digitization. Through data analytics, automation, and modular structures, manufacturers can continue their journey towards Industry 4.0.
