SABIC Uses Blockchain Software to Trace Greenhouse Gas Emissions of Products
Pilot project with Circularise monitors carbon emissions throughout value chain
SABIC has launched a pilot project with Circularise, a Netherlands-based blockchain software provider, to evaluate the use of the latter’s Smart Questioning technology in tracing the carbon footprint of specific material streams from end to end.
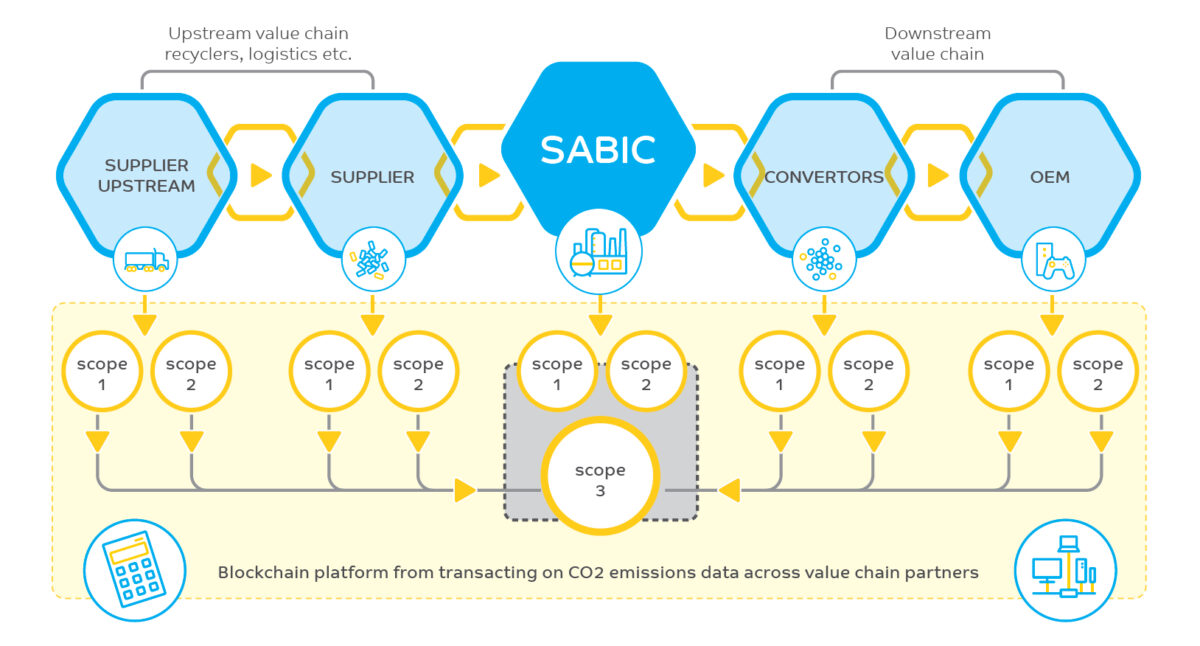
The project will use the Circularise technology (www.circularise.com) to record emissions activity across the value chain by deploying a consistent methodological and reporting framework accepted by industry, specifically, Scope 1 and Scope 2 data captured at the material level, which can be used to generate Scope 3 CO2 emissions for the full value chain of targeted industries.
Data Provide Access to Emissions Reports
The use of Smart Questioning technology will benefit SABIC’s (www.sabic.com) value chain by reducing the administrative efforts associated with data collection and providing access to upstream and downstream data supplied by value chain participants, from recyclers to converters to original equipment manufacturers, among others.
Scope 1, 2 and 3 data are classifications that were developed by the Greenhouse Gas Protocol, an organization founded in 1996 by the World Business Council for Sustainable Development and the World Resources Institute. Scope 1 data cover emissions from sources that an organization owns or controls directly; Scope 2 data are emissions that a company causes indirectly and come from where the energy it buys, and uses, is produced; Scope 3 data encompass emissions that are not produced by the company and are not the result of activities from assets owned or controlled by it, but by those that it’s indirectly responsible for up and down its value chain. Scope 3 emissions include all sources not within the Scope 1 and 2 boundaries.
Blockchain Software Prevents Data Tampering
Generating and reporting Scope 3 emissions is complex and hampered by the availability of reliable data. Accurate data on a company’s carbon footprint requires collaboration and data sharing across multiple value chain partners. Blockchain technology has emerged as a potentially efficient solution to improve the process that can bolster transparency and accountability while minimizing risk across supply chains.
A blockchain is a decentralized, distributed and public digital ledger used to record transactions across many computers so that the record cannot be altered retroactively without the alteration of all subsequent blocks and the consensus of the network.
“As part of this project, Circularise aims to pilot blockchain-powered digital product passports and help businesses to track product emissions on a large scale and over time, generating comprehensive product life cycle emission reports.” Says Mesbah Sabur, founder of Circularise.
“Accurately mapping emissions, especially Scope 3 emissions, will allow SABIC and others to identify and minimize hot spots along the value chain, a critical tool in our pathways to decarbonization,” says Waleed Al-Shalfan, vice president of Polymers Technology and Innovation at SABIC.
The collaboration with Circularise marks SABIC’s second blockchain application project. Last year, the resin supplier launched a pilot project with Finboot, Plastic Energy and Intraplás to evaluate the use of blockchain technology in supporting end-to-end digital traceability of circular feedstock in customer products.
